Confined space work is some the most hazardous in the construction field. You must have appropriate training before you may perform confined space work.
A Confined space is considered to be a space large enough to enter into, has limited means of entry and exit, and is not designed for continuous human occupancy.
Common construction confined spaces are tanks, vessels, bins, silos, boilers, pits, septic tanks, sewers, underground utilities, pipelines, excavations, and similar structures.
It is the responsibility of the employee to follow all instructions pertaining to confined spaces. Employees are never to enter confined spaces unless authorized by training and job duties.
Attendant: an individual stationed outside one or more spaces who monitors the authorized entrants and who performs all attendants’ duties assigned in the permit space program.
Authorized Entrant: an employee who is authorized by the employer to enter a permit space.
Hazardous Atmosphere: an atmosphere that may expose employees to the risk of death, incapacitation, impairment of ability to self-remove (that is, escape unaided from confined space), injury, or acute illness from one or more of the following causes:
- Flammable gas, vapor, or mist in excess of 10 percent of it Lower Flammable Limit (LFL). This information can be found on the SDSs for the product in question
- Airborne combustible dust at a concentration that meets or exceeds the LFL. This information can be found on the SDSs for the product in question.
- Atmosphere oxygen concentration below 19.5 percent or above 23.5 percent.
- Atmosphere concentration of any substance for which a dose or permissible, is published in CFR 1910, Subpart G Occupational Health and Environmental Control, or in Subpart 2 Toxic and Hazardous Substances, of this part and which could result in employee exposure in excess of its dose or permissible exposure to light.
- Any other atmospheric condition that is immediately dangerous to life and health.
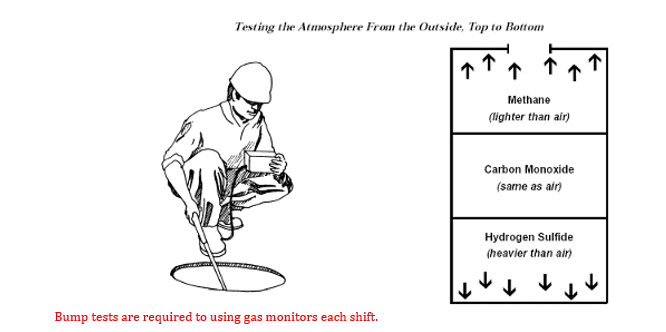
A qualified person shall test spaces a minimum of three (3) times at all levels immediately prior to entry. Below illustrates the common gases found at each of these levels.
Using a calibrated direct-reading instrument with remote sampling capacity, the qualified person shall test for oxygen content, for flammable gases and vapors, and for potential toxic air contaminants, in that order. The testing shall assess for:
- Oxygen level (19.5 % minimum/maximum 23.5 %)
- Carbon Monoxide less than 35 ppm
- Potential flammable hazards (not to exceed 10% of its Lower Flammable Limit (LFL))
- Toxic materials known or expected to be present (Hydrogen sulfide 10ppm Max) (other gases must be less than the known Threshold Limit Values (TLV) for that gas)