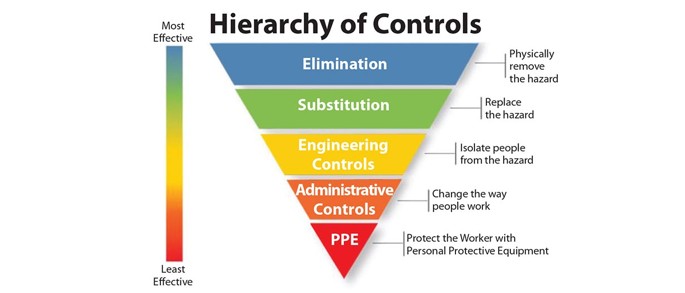
The final line of protection is the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). PPE is used when the risk cannot be reduced enough to provide a safe working environment for the worker. Prior to performing any task, a hazard assessment shall be conducted by the entire crew via Doggett’s Pre-Task Plan (PTP)
Eye Protection

- Safety glasses are required to be worn by all individuals at ALL times. Safety glasses must meet ANSI Z87.1, Practice for Occupational and Educational Eye Protection. Protectors shall be required where there is a reasonable probability of an eye or face injury that could be minimized or prevented by the use of such protection.
- Where there is a reasonable probability of impact from flying objects, a protector with side protection is required.
- Protectors shall be used in conjunction with engineering controls and sound safety practices. Known hazards should be removed or minimized to the extent possible.
- Wearers of prescription (Rx) eyewear will wear eye protection that incorporates the prescription in its design or that can be worn over prescription lenses without disrupting either the prescription eyewear or the protective eyewear. Employees who wear prescription glasses are required to wear side protection that extends from the front to some distance between the front and the wearer’s ear and provides limited protection to the wearer’s eyes from lateral hazards.
- Basic impact protectors (lenses) may be used only in an environment where the known or presumed hazards are of low velocity, low mass and low impact nature.
- High impact protectors must be used in an environment when the known or presumed hazards are of a high velocity, high mass or high impact nature.
- Only clear safety glasses, including prescription eyewear, lenses shall be worn indoor, including parking decks. Tinted/shaded safety glass lenses may be worn outdoors.
- Face shields when worn require high impact safety glasses/goggles worn.
 | Hard-hats are to worn at all job-sites.Hard-hats shall meet the specifications of 29CFR 1910.135 and ANSI Z89.1, Protective Head Wear for Industrial Workers.Electricians’ hard hats are Class E – for utility service, protects head from impact and penetration from falling and flying objects and high-voltage shock and burn. It is mainly used during electrical work. |
At the jobsite, boots are to be worn at all times. At a minimum, the boot must be of hard soles with leather uppers. Boots must extend above the ankle in order to provide proper protection and support. Safety shoes should be sturdy and have impact resistant safety toes, slip resistant protection, and heat resistant soles.
Boots will be composite toe and meet the requirements of ASTM F2413-11.

Caterpillar & Wolverine boots https://www.metboots.com/c-electrical-hazard-boots.html Samples of boots that meet ASTM Electrical Hazard Standard F2413-05
Gloves
 | Gloves are to be worn at all times.Issued gloves are to be minimum cut resistant ANSI level III.Gloves are intended to provide protection from laceration and puncture hazards. |
| Remember This The best way to know if you need hearing protection is to measure the sound levels (in decibels). If you do not have the tools to do this, the next best way is the shout test. If you have to shout to be heard when standing 3 feet (at arm’s length) away from someone, then it’s probably over 85 decibels and hearing protection should be worn. Find the most comfortable hearing protectors (earplugs or earmuffs) and make sure you wear them every time you are around loud noise. If you choose to wear disposable foam earplugs, make sure you insert them properly. If you are not sure how to, then ask your supervisor for training. Avoid inserting or removing earplugs if your hands are dirty, to avoid an ear infection. Wear hearing protection and take breaks from loud noise. Look for signs that identify noise hazards. Ask your employer to consider purchasing quieter equipment in the future. If possible, move your work away from noise sources or move the noise sources away from your work area. Have your hearing tested as soon as possible to have a baseline measurement of your hearing. Have it rechecked during regular doctor visits to make sure you haven’t damaged your hearing. | 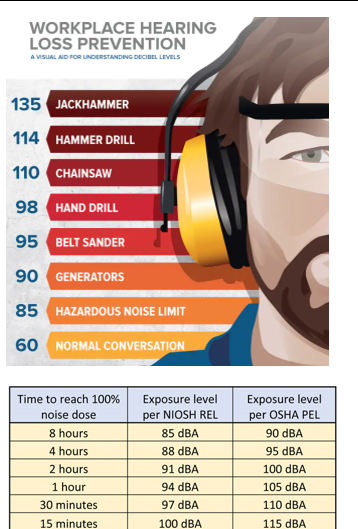 |
- Respiratory protection is required to protect employees who have potential exposure to harmful dust, mists, gases, vapors, or other harmful agents.
- All respiratory protective devices must be approved by the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA), National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) or acceptable to the United States Department of Labor for the specific contaminant to which the employee may be exposed.
- Respiratory protective equipment must be inspected regularly and maintained in good condition. Gas mask canisters and chemical cartridges must be replaced as necessary so as to provide complete protection.
- Used respiratory protective equipment must be cleaned and disinfected before it can be issued to another employee.
- Refer to the Section 2 of the Industrial Hygiene Section of this manual for additional information.
- Personal protective equipment shall be available at all jobsites.
- The supervisors/foremen are required to issue the proper personal protective equipment when needed or required.
- If a supervisor/foreman finds that special personal protective equipment is required, then he/she should contact the Field Safety Specialist or safety management for advice on purchasing and receiving the required personal protective equipment.
